A soffit refers to the finished surface installed on the underside of architectural elements, most notably beneath roof eaves. It plays a crucial role in home design, unifying both aesthetic appeal and practical functionality. The scope of the soffit definition is broad; it includes areas such as archways, staircases, cornices, and balcony undersides, all contributing to a home’s finished and cohesive look, while hiding essential ventilation components.
For homeowners and those interested in architecture, understanding what soffit is in construction is crucial for grasping how it balances aesthetics with the need for durability and airflow.
Soffit panels protect structural elements from moisture and enable essential attic ventilation, helping prevent numerous home issues, as highlighted by industry specialists.
This guide will provide a clear explanation of the soffit definition, outline its most common locations, and address how it differs from fascia boards. Readers will find practical context, real-world expert commentary, and terminology presented in an accessible way.
Many homeowners search for soffit repair or soffit replacement when they notice peeling paint, sagging panels, or holes in the eaves. Small problems often become larger if left untreated.
Early action such as a targeted soffit repair or a soffit board replacement can stop water damage from spreading to rafters and fascia. If you need both trim and ventilation fixed, look for soffit and fascia repair or soffit and fascia replacement services. I will cover common repair steps, DIY options, and when to hire a contractor.

What Is a Soffit in Construction?
In architecture, soffit commonly refers to the underside of structural components, especially the overhanging part of a roof, also called the eaves. The term extends beyond rooflines to include under-ceiling areas, archways, staircases, and balconies. Modern soffit panels often conceal utilities or exposed beams, providing a finished and unified appearance both inside and out.
Technically, soffit serves a dual function in construction: it delivers aesthetic appeal and fulfills practical requirements. The soffit definition in this context covers both exterior applications (like roof eaves and cornices) and interior features (such as dropped ceilings and boxed-in zones). Additional locations include the underbelly of staircases, between built-in cabinets and ceilings, and beneath projecting windows or vent hoods.
- Underside of roof eaves (most common example)
- Ceilings beneath exterior overhangs
- Below balconies or projecting windows
- Recessed or dropped ceilings indoors
- Underneath staircases in entryways or halls
- Beneath arches, often called the “intrados”
- Below bay windows and cornices for added finish
- Areas under vent hoods or raised skylights
- Spaces designed for hidden lighting or HVAC
- Boxed-in zones that cover exposed beams or structures
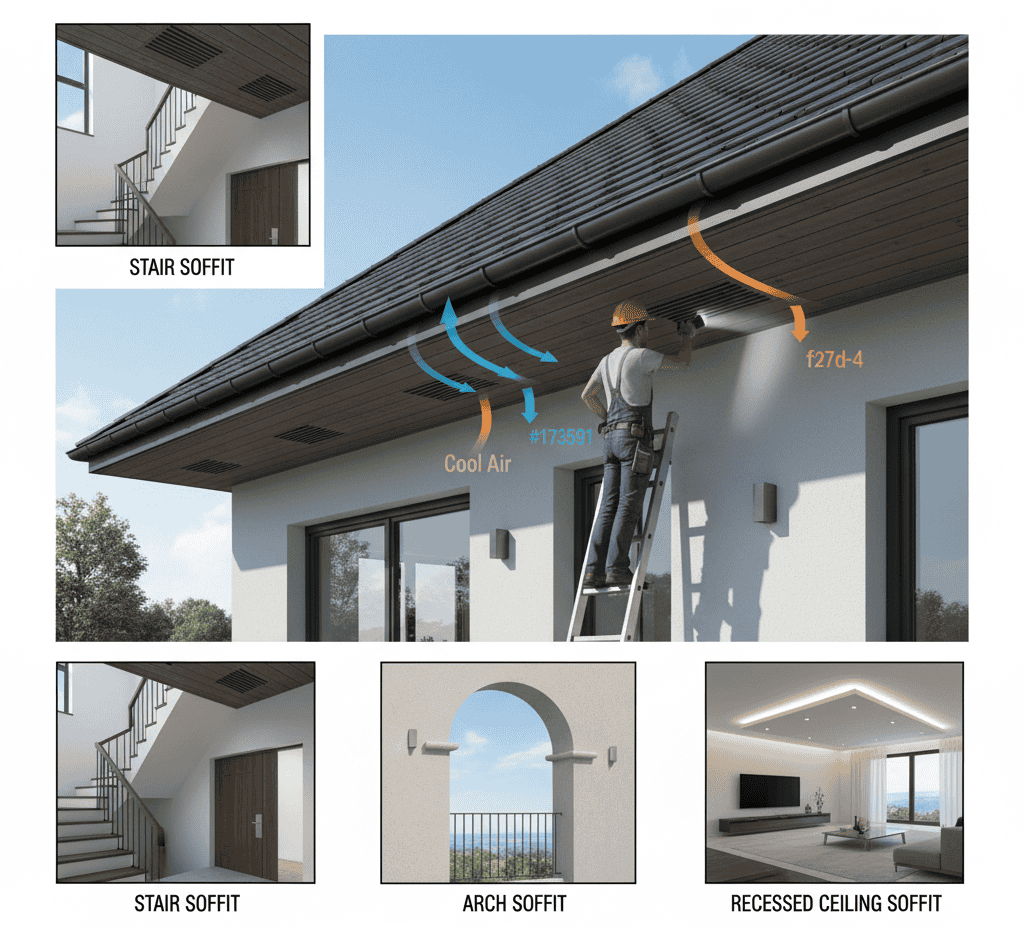
The difference between the general term soffit and its practical application in construction lies in the detail and intention: in building, soffit is the visible or functional enclosure beneath an overhang, with a focus on design and protection.
When soffits get damaged, common fixes include patching small holes, replacing individual panels, or a full soffit replacement when rot or widespread decay exists. Typical repair work is described as soffit board replacement or roof soffit repair.
If the soffit is wooden and suffering from dry rot, a wood soffit replacement is often recommended. Some homeowners choose a vinyl or aluminium replacement because these materials reduce future maintenance. If you are troubleshooting, check for soft spots, insect nests, or missing vent slots as indicators that soffit repair is needed.
Why Soffits Are Essential for Your Home
The core function of the soffit is to protect and regulate. Without reliable soffit and ventilation, homes are exposed to problems like moisture entry, temperature swings, and pests. Soffits protect the underside of roof eaves from rain, snow, and animals, while their impact also extends indoors via the attic ventilation system.
Soffit and ventilation work together, supporting energy conservation and preserving the roof’s vital elements. Panels with vent openings allow air into the attic and promote healthy airflow. This setup helps stop the accumulation of stagnant, humid air, which is essential for stopping mold, wood rot, and roof damage.
The effectiveness of a home’s energy use is directly related to the soffit system’s ability to manage heat and moisture. Soffits channel cool exterior air into attics, keeping attic temperatures stable in every season. This keeps energy bills lower, helps shingles last longer, and reduces the risk of ice dams at the roof edge.
Soffit design also acts as a defense against mold, wood rot, and insects. Materials that are tough and well-sealed stop pests from entering through roof overhangs. At the same time, proper ventilation and drainage minimize rot and moisture damage inside.
- Keeps eaves, rafters, and roof deck dry
- Maintains steady attic airflow for any climate
- Limits condensation, mold, and rot
- Covers entry points for animals or insects
- Promotes uniform attic temperature throughout the year
- Helps insulation work more efficiently and maintains energy ratings
- Boosts shingle life by preventing excessive heat
- Decreases likelihood of ice dams in winter
- Shields wood from sunlight, wind, rain, and snow
- Supports safe and healthy living by reducing air stagnation
- Contributes to extended structural durability
- Lowers the chance of water damage and long-term repairs
- Provides a clean, finished appearance beneath roof edges
- Works with both traditional and modern architecture
- Helps achieve code-required attic ventilation
- Necessary for mold control, especially in humid climates
- Important in well-designed roof systems
- Reduces attic and roof air leakage, saving energy
- Improves attic fan and ventilation system performance
Consistent soffit functionality is key: panels built for airflow as well as protection make a direct difference in lowering maintenance expenses and improving comfort inside the home.
Soffit problems left unattended often require combined work: soffit and fascia repair or a full soffit and fascia replacement. When you see signs such as sagging soffits, holes, or peeling paint, arrange a soffit inspection.
Quick repairs like filling holes or replacing a few panels can be called soffit repairs, while rotted or structural damage may need replacing soffits and associated fascia boards. Addressing problems quickly prevents costly roof eaves repair and reduces the chance of needing major roof and soffit repair later.
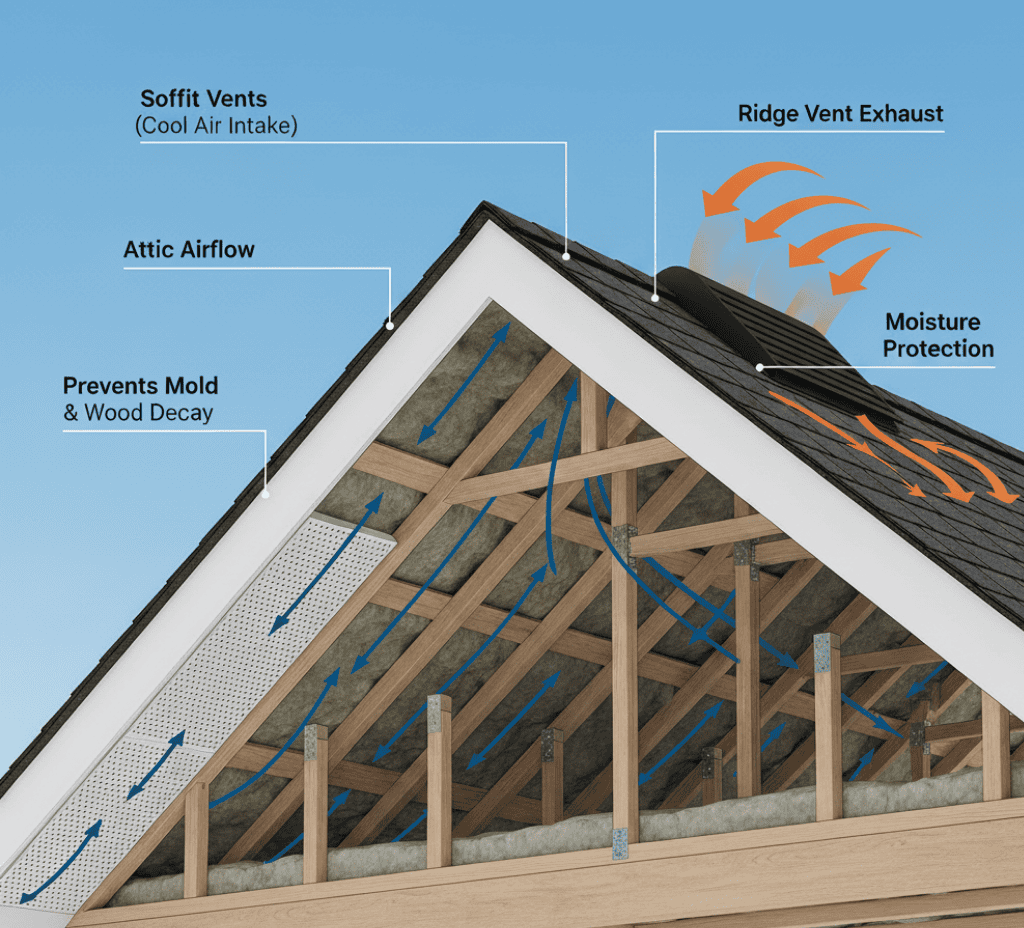
How Soffit Vents Work
Soffit vents are essential to attic airflow. These vented or slotted panels are installed along the eaves to admit outside air, which rises through the attic toward the roof or ridge vents. This flow removes excess heat and moisture, creating continuous ventilation and maintaining a dry, healthy roof structure.
• Soffit vents provide exterior air to the attic
• Air moves up between rafters, leaving through roof or ridge vents
• This cycle keeps attic temperature near outdoor levels
• Keeps insulation dry, reducing wasted energy
• Hinders mould, wood decay, and mildew
• Increases the life of the roof and framing
• Reduces shingle temperature swings, minimising stress
• Meets building code standards for attic airflow
• Lowers attic heat in summer, easing air conditioning demand
• Prevents condensation during cold weather
Adequate vented soffit area lets the attic benefit from constant air circulation, which is needed for the home’s durability and residents’ well-being.
Common soffit vent issues include clogged vents, broken vent slots, or damaged vented panels. For these, a soffit vent repair or a replacement soffit vent service is needed. Blocked vents reduce intake airflow and may lead to attic moisture and mould.
When replacing soffit vents, choose panels and vent patterns that meet local attic ventilation code. If you spot birds nesting behind the vents, consider soffit vent screens or soffit repair to seal access points.
Identifying Soffit vs Eave on Your Home
Differentiating soffit from eave starts by examining your home’s roof overhang. The eave is the portion of the roof that stretches beyond exterior walls, creating the outer overhang around the building. The soffit is the flat, finished enclosure mounted beneath this overhang. The eave is a structural component, while soffit boards provide sealing and protection for the area underneath.
To spot the soffit on your home, walk along the exterior and look upward at the roof’s edge. If you see a smooth or vented panel covering the underside of the overhang, this is the soffit. If the rafters or beams are visible and unprotected, there is no soffit present. Closed or boxed-in areas beneath the eaves indicate soffit installation, with vent patterns or embossed finishes for added detail. Older homes might reveal open rafters, whereas most newer builds use enclosed, vented soffits.
• Locate where the roof protrudes beyond the wall, this is the eave
• Look underneath for a panel this is the soffit
• Panels with vent holes or embossing show soffit is installed
• Open rafters mean an exposed eave and no soffit
• Boxed or enclosed areas below roof edges are soffited
• Find vent slots for signs of attic ventilation
• Soffit often matches the trim color for a unified look
• Larger houses may use soffit under porches or bay windows too
• Check for signs of wear, missing, or damaged panels during inspection
• Eave: projecting roof area; soffit: finished surface underneath
This simple inspection helps you tell the difference between soffit and eave configurations and understand their effect on your home’s attic airflow and exterior style.
If you find damaged or missing panels, common next steps are replacing soffit panels or soffit repair. Removing a single panel for inspection is often enough to check rafters and eave condition. For larger damage, such as rotted soffits or rotted eaves, contractors perform the replacement of soffits and sometimes replace fascia boards at the same time. If you are unsure, search for soffit and fascia replacement near me or ask a local roofing company for an assessment.
Types of Soffit Materials and Panels
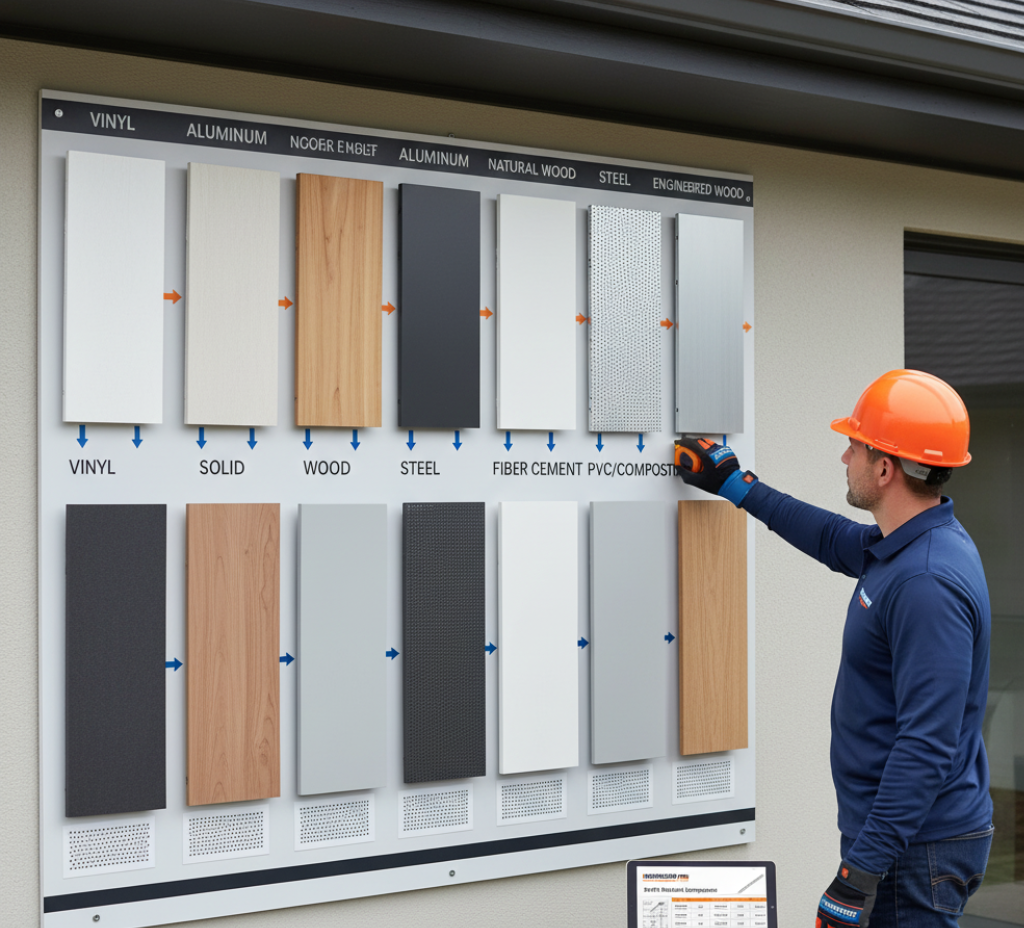
The choice of soffit material has a direct effect on durability, style, and airflow control. Modern soffit panels are produced from a wide variety of materials, each offering unique benefits and trade-offs suitable for different weather and appearance requirements. Here’s a breakdown of the primary soffit materials used today and their respective characteristics:
1. Vinyl soffit
Lightweight, affordable, and requires little ongoing care. Available vented or solid, and in numerous colours; may fade or crack in severe weather.
2. Aluminium soffit
Extremely sturdy, doesn’t rust, and works well for vented designs. Fire- and insect-resistant, but can be dented by impact.
3. Wood soffit
Ideal for classic or premium homes. Can be stained or painted for custom looks. Needs regular maintenance and is prone to decay.
4. Fibre cement soffit
Lasts long while resisting moisture and insects. Available in smooth or with wood-grain. Has a higher initial cost, but limited maintenance requirements.
5. Steel soffit
Offers top-level strength and longevity; handles harsh elements well, but is heavier and more difficult to install.
6. PVC or composite
Looks like wood but is easier to care for and withstands the elements. Fully customizable in style and vent designs.
7. Engineered wood and beaded/wainscot panels
Distinctive finishes, with beaded trim often used to recreate traditional aesthetics in historic properties.
8. Perforated/slotted soffits
Purpose-built for attic airflow while maintaining insulation and protection against pests.
9. Solid soffit panels
Used where airflow isn’t a concern, providing only visual refinement and protection.
10. Custom panels
Manufactured for specific requirements, including climate-specific adaptation or matching unusual siding types.
• Eco-friendly, recyclable panel options are available
• Panels can be coordinated in colour or made ready for painting
• Choose between exposed or concealed fastener arrangements

Material choice affects repair and replacement strategies. For example, vinyl soffit repair usually involves replacing the damaged vinyl panel, while wood soffit repair often requires cutting out rotted sections and installing new trim. If you have rotted soffit or rotten soffits, consider a full wood soffit replacement with pressure-treated wood or upgrading to vinyl or fibre cement to reduce maintenance.
For metal panels, aluminium soffit repair may require panel straightening or replacement of dented runs. When planning work, ask for a soffit replacement estimate and clarify if the job includes removing old soffit, replacing soffit vents, and repairing attached fascia.
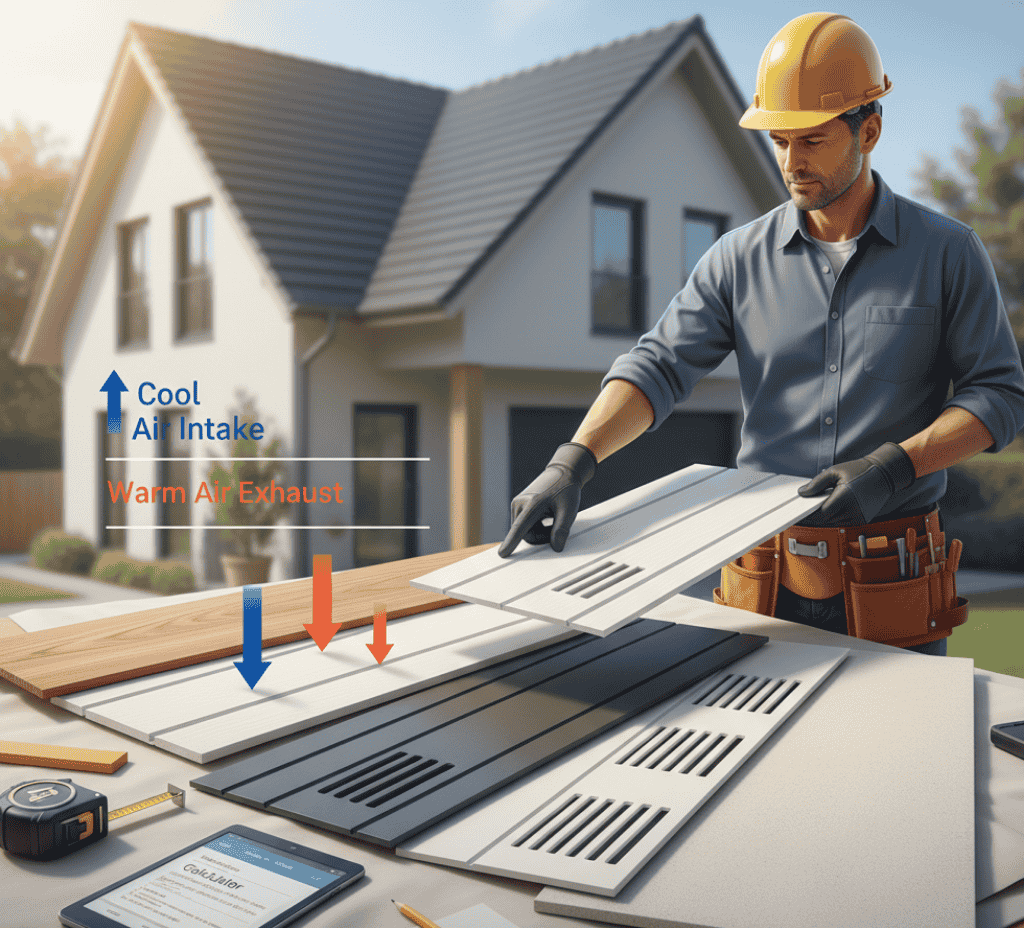
Selecting and Planning Soffit Panels
Preparing for soffit installation starts by reviewing your home’s trim, siding, and degree of weather exposure. Select soffit materials that align with both how you want your exterior to look and the performance features required. In humid climates, vented panels with moisture resistance are best. In drier regions, a solid or decorative soffit can be chosen for added appearance. Always coordinate soffit systems with guttering and roof flashing for smooth integration.
• Decide if vented or solid panels fit your environment and attic airflow requirements
• Pick soffit types (wood, vinyl, aluminium, or fibre cement) to match upkeep needs and styles
• Harmonise colours and surface finishes with other trim, siding, or fascia
• Follow manufacturer guidelines for panel cutting and installation reliability
• Account for code standards related to attic ventilation and airflow rates
• Use a soffit calculator to assess needed quantities and stay within budget
• Review existing gutters and roof for compatibility before adding soffit
• Check for any unique architectural requirements, including corners or unusual overhangs
• Match panel strength to local weather demands, especially in storm-prone zones
Planning prevents mismatched soffit installations, supporting consistent roof protection and attractive curb appeal.

If you plan a DIY soffit replacement, prep includes ordering exact panel lengths and soffit clips or fasteners, and confirming soffit joist spacing. For larger jobs, search for soffit and fascia replacement companies near me. Contractors often quote combined fascia and soffit work because replacing fascia and soffits together reduces labour and ensures a proper seal. When budgeting, include costs for soffit removal, disposal, and any necessary fascia board repair. If you have open rafters, ask whether soffit installation requires new framing or eave replacement.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a soffit on a house?
A soffit is the material installed underneath your roof’s overhang. It covers exposed rafters, protects the roof structure from rain and pests, and allows ventilation through soffit vents. Without soffits, homes are more vulnerable to water damage and energy loss.
2. How do I know if my soffit needs repair?
Signs that you may need soffit repair include:
Peeling paint or water stains
Sagging or cracked soffit panels
Pest infestations (birds, squirrels, wasps)
Poor attic ventilation or rising energy bills
If you notice these issues, schedule soffit repair or replacement before damage spreads to fascia or rafters.
3. What is the difference between soffit and fascia?
The soffit is the horizontal board under the roof overhang, while the fascia is the vertical finishing board at the roofline that supports the gutters. In many cases, contractors recommend soffit and fascia repair together to ensure the whole roof trim system works properly.
4. How much does soffit replacement cost?
The average cost of soffit replacement ranges from $20–$30 per linear foot. Vinyl is usually the most affordable, while wood and fibre cement cost more. If fascia repair or gutter replacement is needed at the same time, the total cost can increase significantly
5. Can I repair a rotted soffit myself?
Minor soffit repair, like repainting or sealing, can be a DIY job. However, rotted soffit repair often involves replacing damaged panels, which is best handled by a professional. Improper repairs may lead to recurring moisture issues and expensive roof damage.
6. Do all houses have soffits?
Not all houses have soffits. Older homes may feature open rafters without coverings. However, most modern homes include soffits to protect against moisture and pests, improve ventilation, and enhance curb appeal.
7. What materials are best for soffit replacement?
Common soffit materials include:
Vinyl – affordable and low maintenance
Aluminium – durable and weather-resistant
Wood – traditional but requires frequent wood soffit replacement if exposed to moisture
Fibre Cement – long-lasting and fire-resistant
The best choice depends on climate, budget, and desired appearance.
8. How long do soffits last?
With proper maintenance, vinyl and aluminium soffits can last 20–30 years, while wood soffits may need replacement in as little as 10 years if exposed to high moisture. Regular inspections and timely soffit board replacement extend their lifespan.
9. What happens if soffit vents are blocked?
Blocked soffit vents reduce attic ventilation, causing higher energy bills, mould growth, and roof deterioration. Regular soffit vent repair and cleaning ensures proper airflow and protect your home’s structure.
10. Can soffit and fascia be replaced at the same time?
Yes, soffit and fascia are often replaced together since both are part of the roof trim system. Soffit and fascia replacement ensures a consistent look, better protection, and reduced labour costs compared to repairing them separately.
Conclusion
Soffit panels are more than a finishing detail; they support vital airflow for attics, protect key home structures, and complete the exterior appearance. The definition of soffit centres on its placement beneath roof overhangs and its role in bridging attractive design with core building needs.
Choosing the correct soffit materials significantly affects attic ventilation, roof lifespan, and blocking moisture or pests. Whether considering vinyl, aluminium, wood, or fibre cement panels, coordinating soffit with the home’s styling and local weather challenges increases both *service life and performance.
For property owners, giving attention to soffit installation and regular care helps protect both home value and structural integrity. For additional explanation of the soffit and fascia connection, review this recommended resource on What is Fascia & Soffit: Understanding Exterior Trim, and take steps to guard your home from environmental exposure year-round.
If you notice signs of soffit damage, do not delay. Start with a visual inspection for holes, sagging, or stains. For small issues, a targeted soffit repair or soffit vent repair may be enough. For larger or widespread deterioration, schedule soffit replacement and consider combined fascia and soffit replacement to ensure a watertight roofline. Search for soffit and fascia replacement near me to find local pros or request quotes from siding and roofing contractors.








